Contents
Types Angles
Supplementary and Complementary Angles
Interior and Exterior Angles
Vertical Angles
Angles Formulas and Notes
Types of Angles
Straight Angle
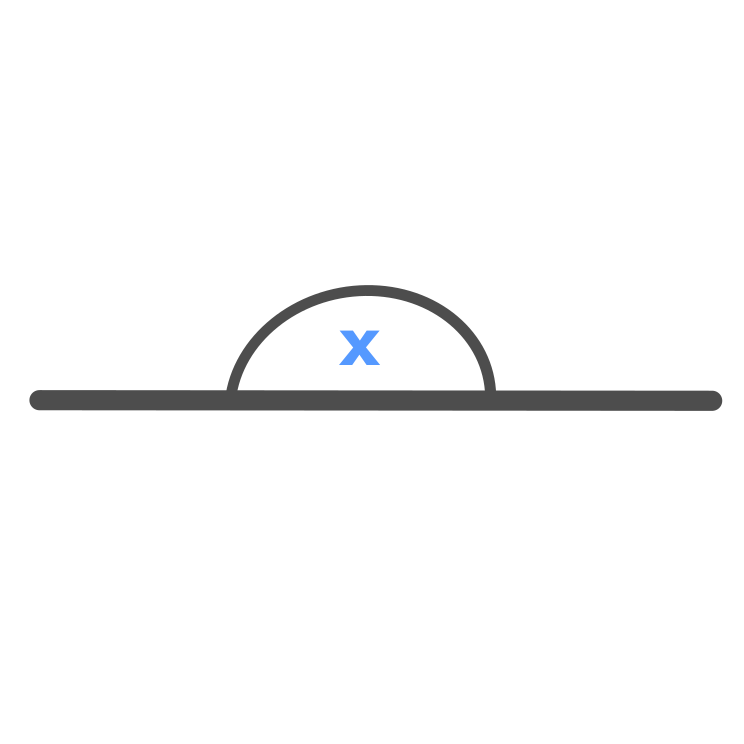
Straight Angle \displaystyle = x = 180 \degree
Acute Angle
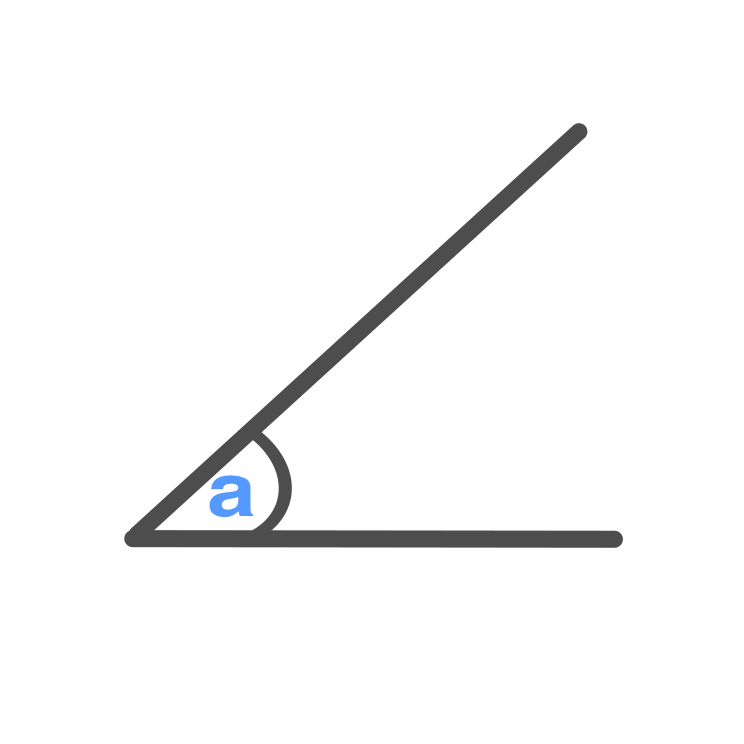
Acute Angle \displaystyle = a
\displaystyle a < 90 \degree
Obtuse Angle
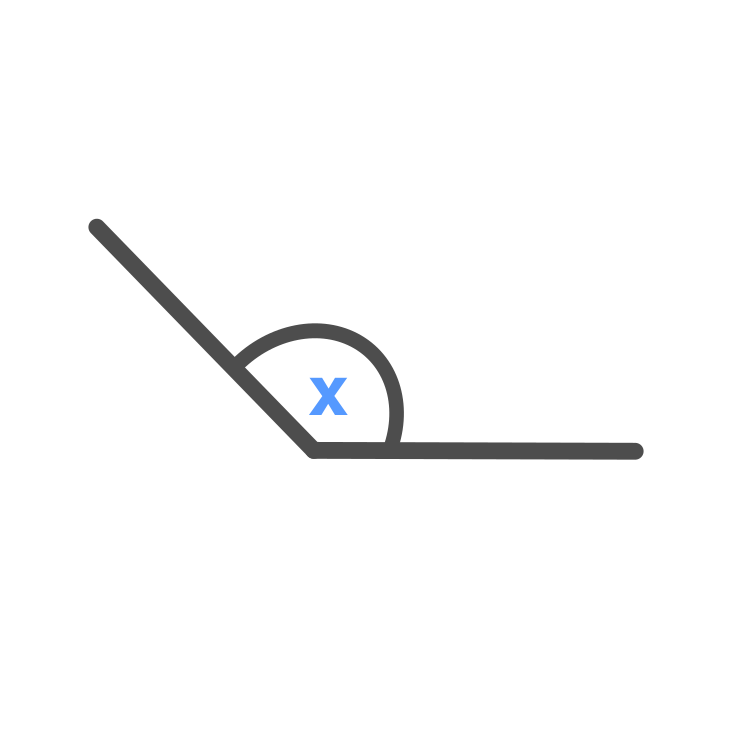
Obtuse Angle \displaystyle = x
\displaystyle 90 \degree < x < 180 \degree
Right Angle
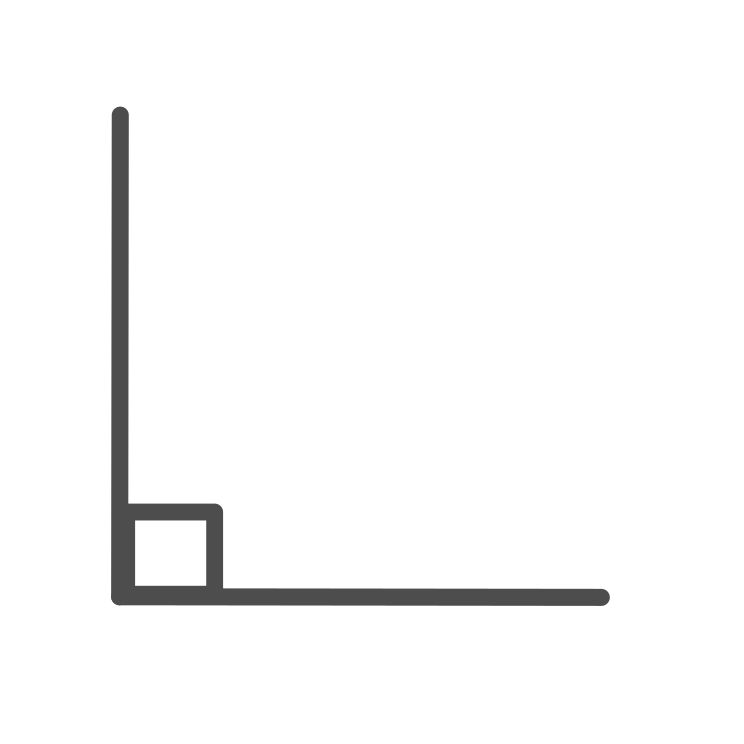
Right Angle \displaystyle = x = 90 \degree
Reflex Angle
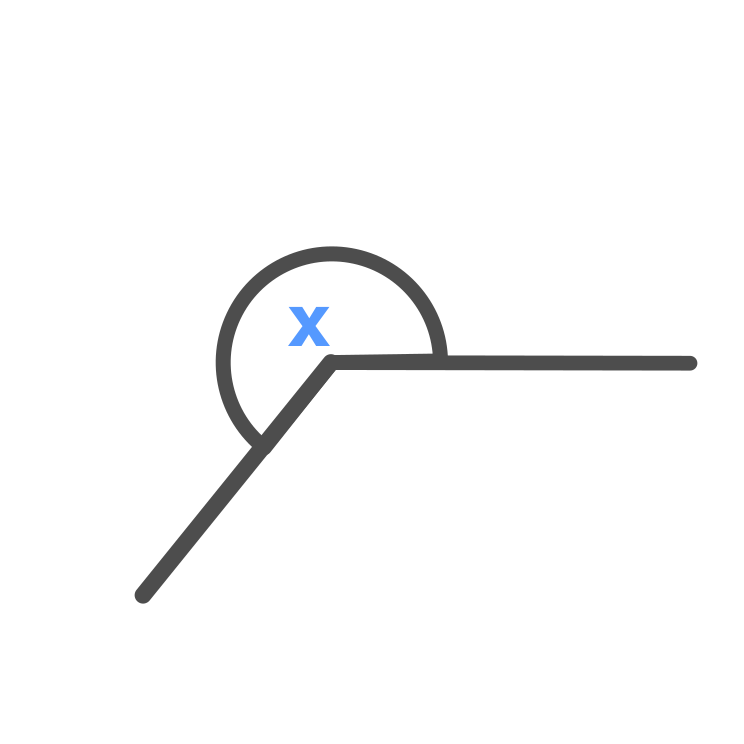

Reflex Angle \displaystyle = x
\displaystyle 180 \degree < x < 360 \degree
Full Angle
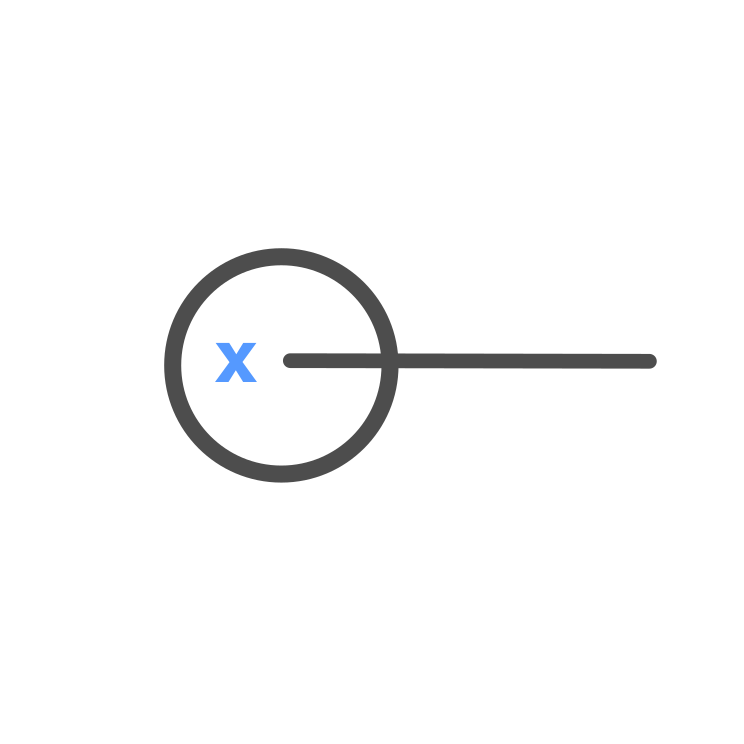
Full Angle \displaystyle = x = 360 \degree
Supplementary and Complementary Angles
Supplementary Angle
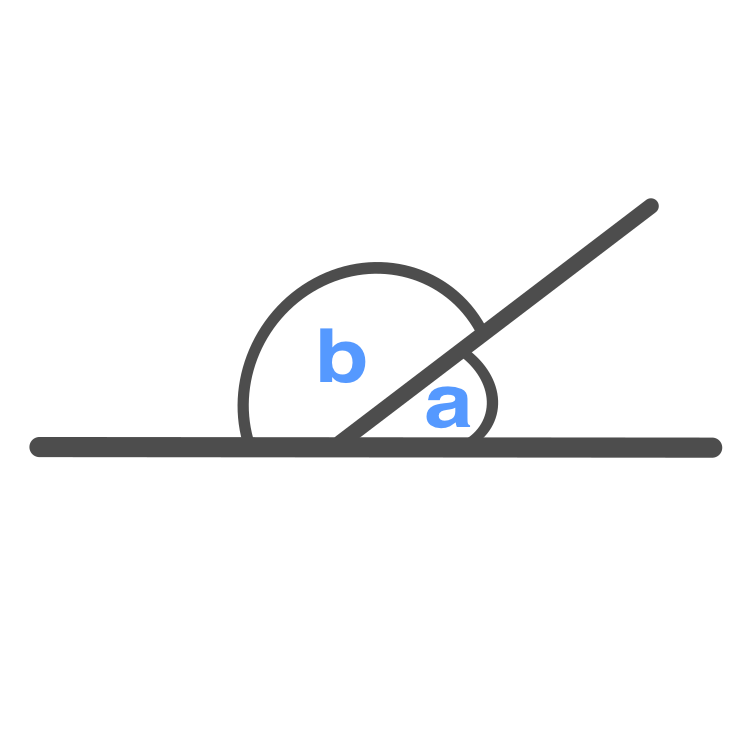
Two angles that have a sum of 180°
\displaystyle a + b = 180 \degree
Complementary Angle
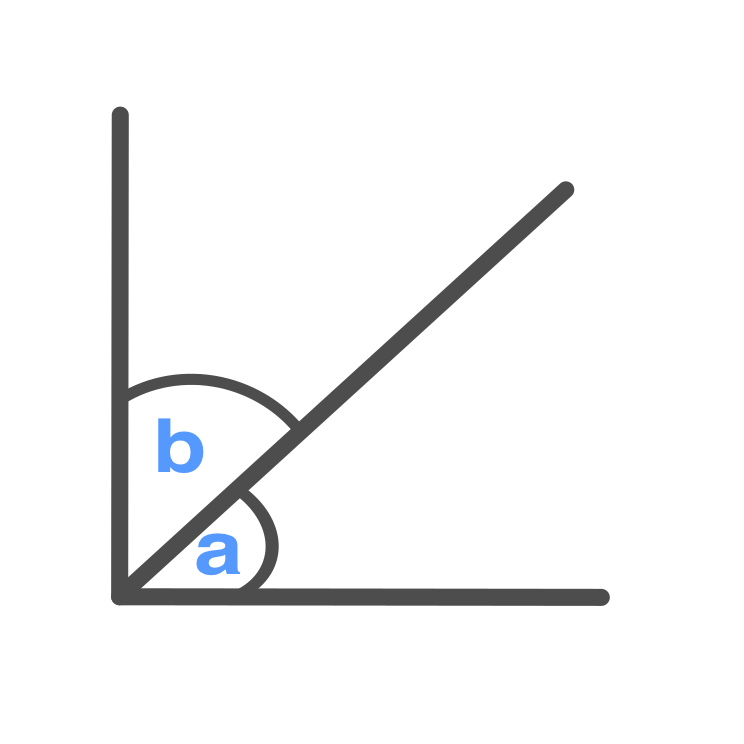
Two angles that have a sum of 90°
\displaystyle a + b = 90 \degree
Interior and Exterior Angles
Consecutive Interior Angles
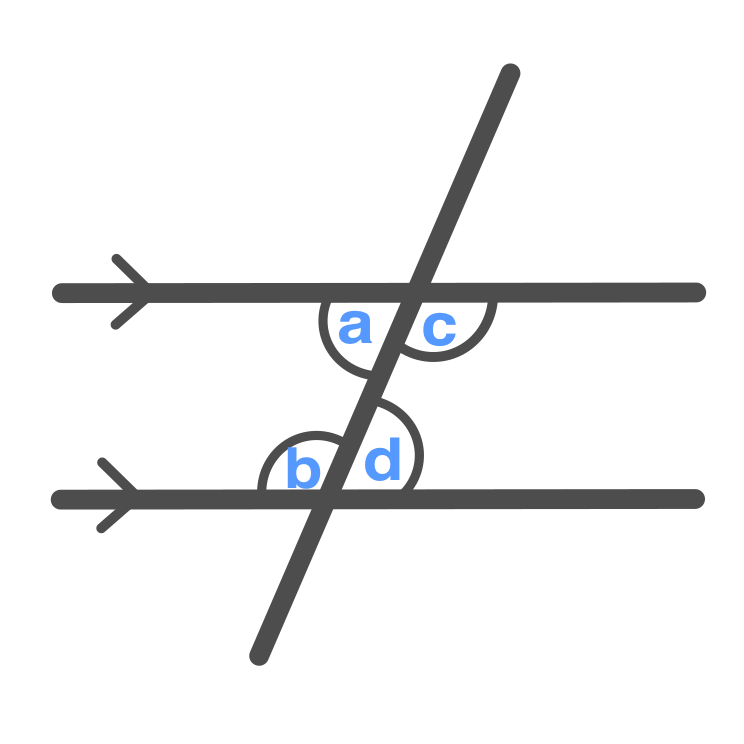
\displaystyle a + b = 180 \degree
\displaystyle c + d = 180 \degree
Alternate Exterior Angles
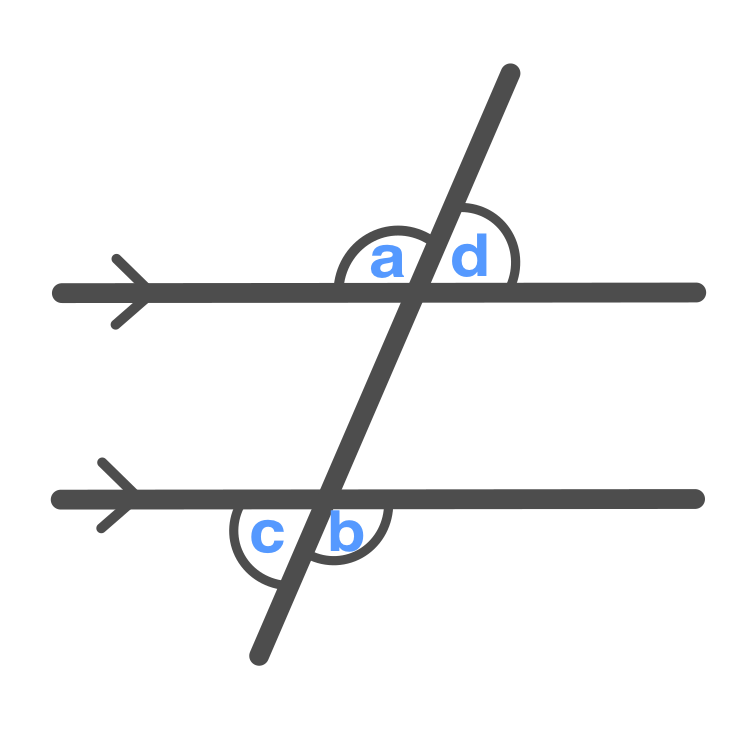
\displaystyle a = b
\displaystyle c = d
Alternate Interior Angles
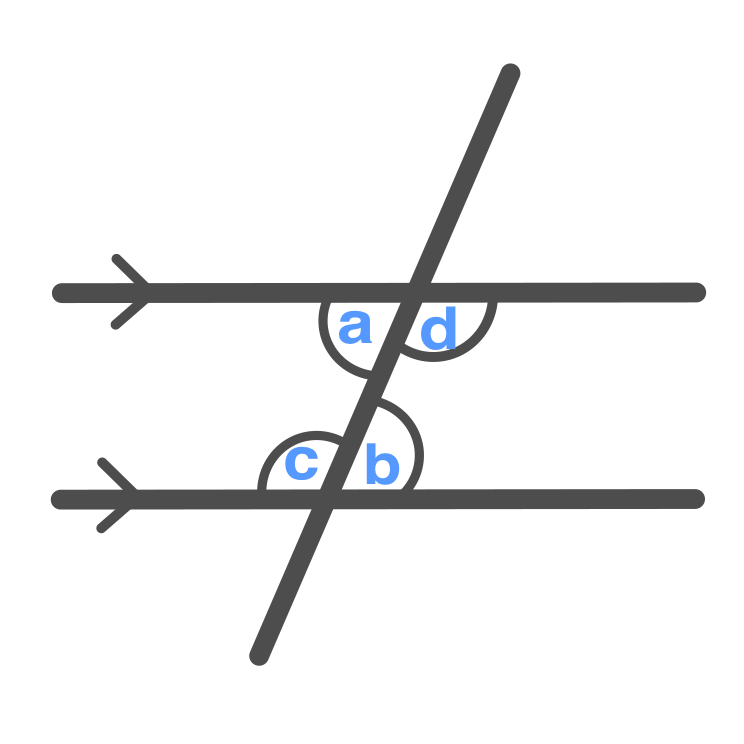
\displaystyle a = b
\displaystyle c = d
Corresponding Angles
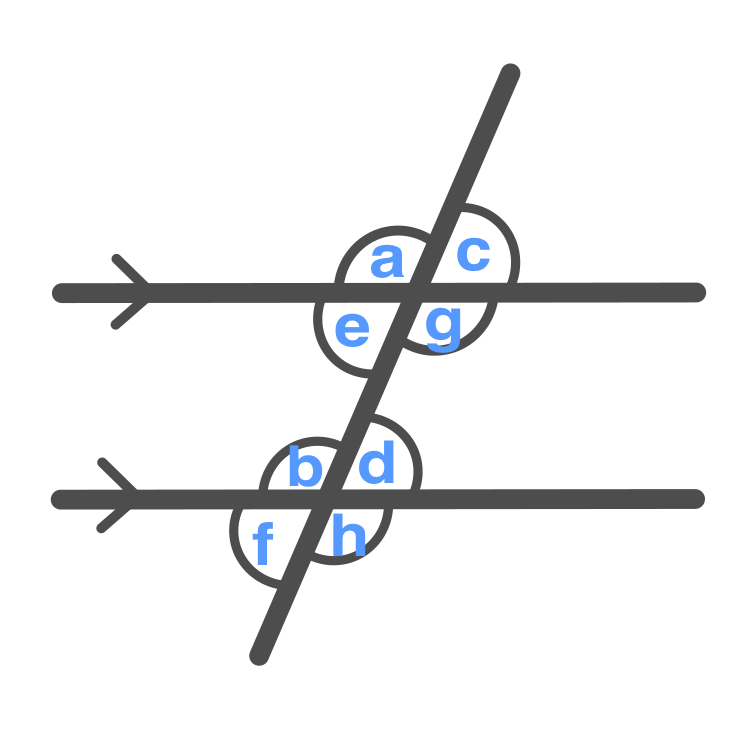
\displaystyle a = b, c = d
\displaystyle e = f, g = h
Vertical Angles
Vertical Angles
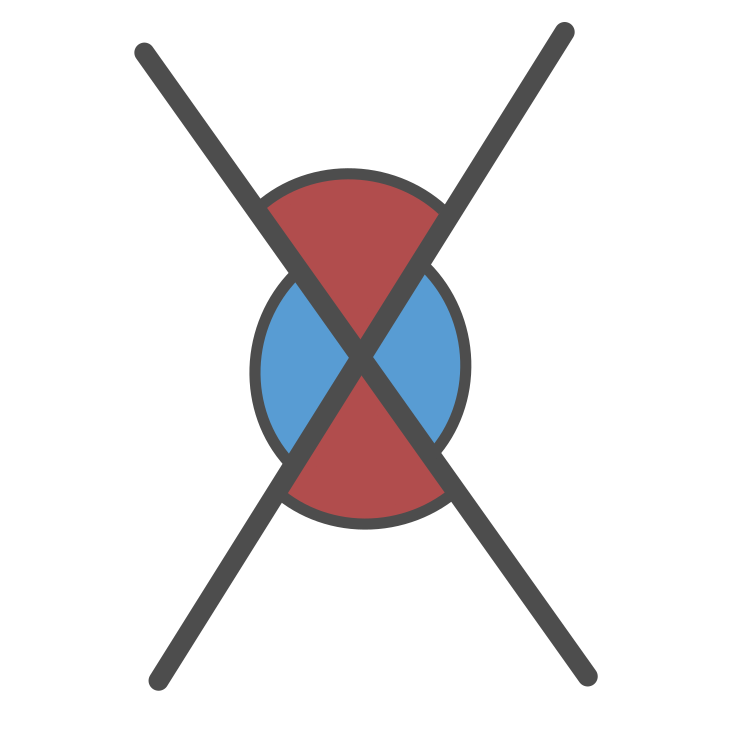
When two lines intersect, they form 4 angles. The verical lines are equal in measure.
